Spring
2016
grainswest.com
37
something similar to the PMRA, or by referring to the global
MRL database known as Codex Alimentarius, or Codex, with all
risk assessment done by the World Health Organization.
Because each country decides on its own way to deal with
MRLs (or which products have them), the MRL regulatory
layer can cause headaches in the grain trade. In the case of a
new product, there’s always a time lag—one or two growing
seasons, typically—between a product’s registration in the
country it is to be used in and the establishment of a Codex
MRL in exporting countries. The second hiccup can occur
when a mature product is destined for markets where the MRL
is zero or defaults to zero in the absence of a set level.
MISSING AND MISMATCHED MRLS
Some products carry a very low risk of any residues ever being
present—think seed treatments—but most products, especially
those used later in the season, are likely to leave some tiny
residue behind. That’s where an MRL of zero causes problems.
“Here’s the trouble with zero,” said Cam Dahl, president of
Cereals Canada. “We can now detect residues down to parts
per billion. To put that in perspective, that’s equivalent to one
second in 32 years.” A tiny speck of residue from a combine
hopper, a bin, an elevator or a shipping vessel could be
detected and, if there is no MRL in place, could cause shipping
disruptions.
MRLs have been around a long time, Dahl said, but testing
equipment has become more and more precise. Because of
this, zero has become too great a risk for exporters. What’s
the answer? Dahl said grower groups and commodity
organizations are working hard with Canada’s trading
partners to avoid absolute zeros for MRLs and to improve
communication throughout the value chain.
In the meantime, however, approved MRLs simply cannot
be exceeded, Dahl said. “A rejected vessel at port isn’t just a
huge cost for the exporter, Canada’s global reputation as an
exporter could also suffer,” he said.
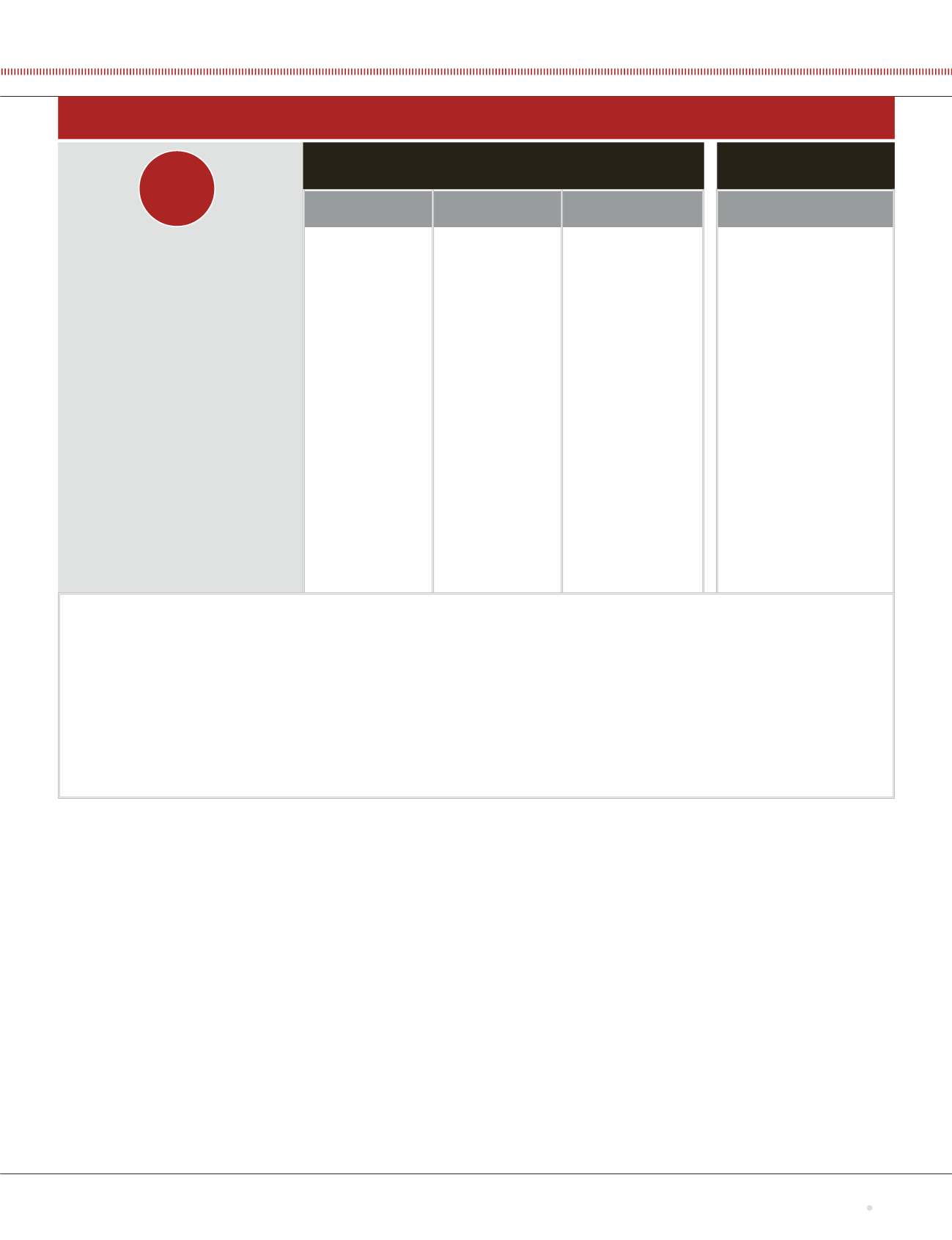
Wheat, food-grade oats, and malt barley market awareness of farm applications
OK
: Maximum residue limit (MRL) is set at an acceptable tolerance level for export to the specified market. Follow label directions carefully, as even minor deviations could result
in market access issues.
Caution
: MRL is set at a low limit, which requires users to follow label directions carefully, as even minor deviations could result in market access issues and/or MRLs are set for
limited markets. Consult with your exporter or processer for proper usage.
Caution/STOP
: MRLs are set at low limits or for limited markets. Consult with your exporter or processer for proper usage.
STOP
: Product is not registered for use in Canada or MRLs have not been established for the specified market. Consult with your exporter/processor on whether or not it will
accept your grain before applying these products.
Disclaimer: This table is accurate as of January 2016, and includes a sample of Canada’s largest cereal export countries, but does not include all of Canada’s cereal export
markets. Changes may occur after January 2016; consult with your exporter/processor prior to using any of the products/active ingredients described above.
For more information on pesticide use in cereals, consult keepingitclean.ca.
Market
European Union
Countries that rely on Codex
MRLs (e.g., Algeria, Bangladesh,
Columbia, Morocco, Peru and
many others)
Japan
United States
Mexico
China
Wheat
Pre-harvest glyphosate
(e.g., Roundup)
Pre-harvest glyphosate
(e.g., Roundup)
Chlormequat chloride
(e.g., Manipulator)
Pre-harvest Saflufenacil
(e.g., Kixor)
Malt barley and
food-grade oats
Caution:
Follow label carefully
OK
Caution:
Follow label carefully
OK
Caution:
Follow label carefully
Caution:
Follow label carefully
Caution: Consult with your
exporter/processor
Caution: Consult with your
exporter/processor
Caution: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
Caution: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor
STOP: Consult with your
exporter/processor


