use and resistance in
cattle?
Worried about
antibiotic
It’s important to us too.
WHERE DOES
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
COME FROM?
When antibiotics are used, bacteria that are responsive to the
drug are killed, and bacteria that aren’t responsive (are resistant)
survive and reproduce.
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
HAPPENS NATURALLY
The Lechuguilla Cave
in New
Mexico has bacteria that have
lived in complete isolation for
more than four million years.
When treated with a variety of
antibiotics, many of these
bacteria were naturally resistant.
1
ALL
BEEF
IS ANTIBIOTIC
FREE
A specified withdrawal time must pass after the
last treatment to ensure that there are no antibiotic
residues left in the beef. The Canadian Food
Inspection Agency regularly tests for residues. In
2013, over 99.9% of both domestic and imported
beef products were free from residues. If residues
are found, the beef is not allowed to enter the food
chain.
11
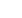
For a person to get an antibiotic resistant infection from eating beef,
a number of
UNLIKELY
things must happen:
HOW DIFFICULT IS IT TO GET A
RESISTANT INFECTION?
Producers also have a responsibility to
use antibiotics with good judgment.
Surveillance
7
indicating low resistance
in cattle to antibiotics of importance in
human medicine shows they are doing
just that. Canada's Verified Beef
Production
TM
program outlines
responsible practices for producers,
and provides training on how to use
antibiotics properly.
13
Previous research showed no
predictable or uniform increase
in resistance between cattle
raised with the use of
antibiotics and those raised
without.
14
Antibiotic use in agriculture is
just one small part of the whole
antibiotic resistance picture that
also includes humans and
pets.
15,16,17
X
animal gets an
antibiotic
antibiotic resistant
bacteria develops
in animal
1
2
3
bacteria survives multiple
food safety controls
during processing
4
bacteria survives
cooking
5
bacteria
causes illness
in person
6
illness is severe
enough to warrant
medical attention
7
Doctor prescribes
antibiotic
8
illness fails to respond
to treatment because
bacteria is resistant to
prescribed antibiotic
12
If beef is cooked properly, the antibiotic resistant bacteria die – breaking the chain
of unlikely events. The probability of human illness in the U.S. due to drug resistant
food poisoning (campylobacteriosis) is about one in 236 million.
12
Being killed by an
asteroid is 1000 times more likely.
18
Regardless
of production
system, beef is an
important part of a
healthy diet
.
Producers take their
ethical responsibility
to protect the health
and welfare of their
families and animals
very seriously, which
includes using
antibiotics when
appropriate.
WHY ARE
ANTIBIOTICS
USED IN CATTLE?
PREVENTION
Preventing infection can
reduce the need to use
more powerful antibiotics
if the disease becomes
more serious. Preventive antibiotics
are also used in human medicine, like
with people who are exposed to
bacterial meningitis.
2
TREATMENT
AND CONTROL OF DISEASE
Cattle sometimes get
sick, just like people,
pets, and other livestock.
Antibiotics can help protect animal health
by limiting the spread of disease.
3
Ensuring animal welfare:
providing care to sick cattle,
including using antibiotics
when appropriate, is the
humane thing to do.
GROWTH PROMOTION
A category of antibiotics
called ionophores
help boost growth in
cattle. Ionophores are not
used in human medicine, and work
differently than medically important
antibiotics.
There is no evidence that
use of ionophores causes increased
resistance to antibiotics used in
human medicine.
3,4
1
ANTIBIOTICS
IN FEED
Just because an
antibiotic is used in
feed does not mean
it is being used to
promote growth. It is
often better for sick
animals to be treated through
feed rather than aggravating
their illness with stress from
multiple injections.